
They allow administrators to set the amount of information each user can store on a specific drive or partition. NTFS supports disk quotas, which are a means of controlling the storage space available on a drive or partition.
It supports large size partitions, with a theoretical maximum size of a whopping 16 EiB (exbibytes) minus 1 KB, which is approximately 1152921 TB (terabytes)! However, the maximum partition size accepted by Windows operating systems is of 256 TB, which is still a considerable value. It offers security, by letting you set permissions on files and folders, so that only set users and groups of users can access them. It can also remap bad sectors by moving recoverable data from such sectors to healthy ones, and by tagging the bad sectors as not to be used. It can restore the consistency of the file system in case of a power loss or system failure. Some of the most important are the following: NTFS is a file system that offers plenty of advantages. NTFS 3.1 was used in Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8 and 8.1, and it is still being used in Windows 10. Although it had received many new features, the core NTFS version has not changed since then. NTFS 3.1: was released with Windows XP in 2001. NTFS 3.0: was first introduced in Windows 2000, which was available to consumers in the year 2000. NTFS 1.2: launched with Windows NT 4.0 in 1996. NTFS 1.1: was released in 1995, with Windows NT 3.51. NTFS 1: the first release that came to see the world when Windows NT 3.1 was launched in 1993. The major NTFS versions are the following: NTFS as a file system has evolved during its lifetime, as Microsoft kept improving on its initial version and released a series of updates over the years. NTFS was the answer to all these problems and more: it provided better support for metadata, better performance because of its improved data structuring, more reliability and so on. Also, it did not offer any data protection in case of a power outage. 
However, FAT32 had its limitations, such as the fact that it could work only with files smaller than 4GB and partitions with a maximum size of 8TB.
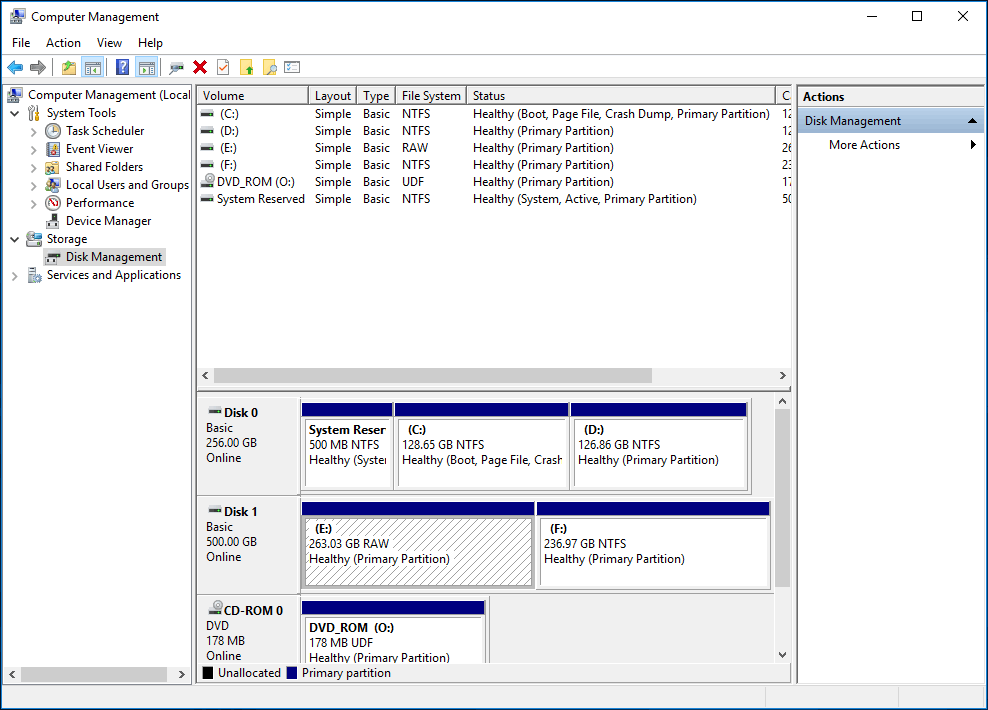
Before NTFS, the Windows operating systems used the FAT32 file system. Because it was created to work with the Windows NT family of operating systems, Microsoft called it the NT File System, which became NTFS in its abbreviated form. It was first introduced in July 1993, with the release of Windows NT 3.1. NTFS is a file system that was developed by Microsoft. NTFS is an acronym for NT File System or New Technology File System and refers to a file system used by the operating system to identify how files are stored, named and organized on a hard-disk drive (HDD), solid-state drive (SSD), USB memory stick, microSD card and other similar storage devices.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
